helm-charts
kafka
A Helm chart for Confluent Kafka on Kubernetes
Introduction
This chart bootstraps a Kafka Cluster using the Confluent stable version.
Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform that:
- Publishes and subscribes to streams of records, similar to a message queue or enterprise messaging system.
- Stores streams of records in a fault-tolerant durable way.
- Processes streams of records as they occur.
Developing Environment
| component | version |
|---|---|
| Podman | v4.3.1 |
| Minikube | v1.28.0 |
| Kubernetes | v1.25.3 |
| Helm | v3.10.2 |
| Confluent Platform | v7.3.0 |
Installing the Chart
Add the chart repository, if not done before:
helm repo add rhcharts https://ricardo-aires.github.io/helm-charts/
To install the chart with the release name kafka:
$ helm upgrade --install kafka rhcharts/kafka
Release "kafka" does not exist. Installing it now.
NAME: kafka
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Nov 22 10:30:47 2022
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
** Please be patient while the kafka chart is being deployed in release kafka **
This chart bootstraps a Kafka Cluster made of "3" brokers using the Confluent stable version that can be accessed from within your cluster:
kafka-headless.default:9092
More info:
https://ricardo-aires.github.io/helm-charts/charts/kafka/
$
By default, it will also install the zookeeper.
If an external Zookeeper Ensemble is to be used turn
zookeeper.enabledtofalseand include thezookeeper.url.
These commands deploy Kafka on the Kubernetes cluster in the default configuration. The Parameters section lists the parameters that can be configured during installation.
The chart will create the next resources, by default:
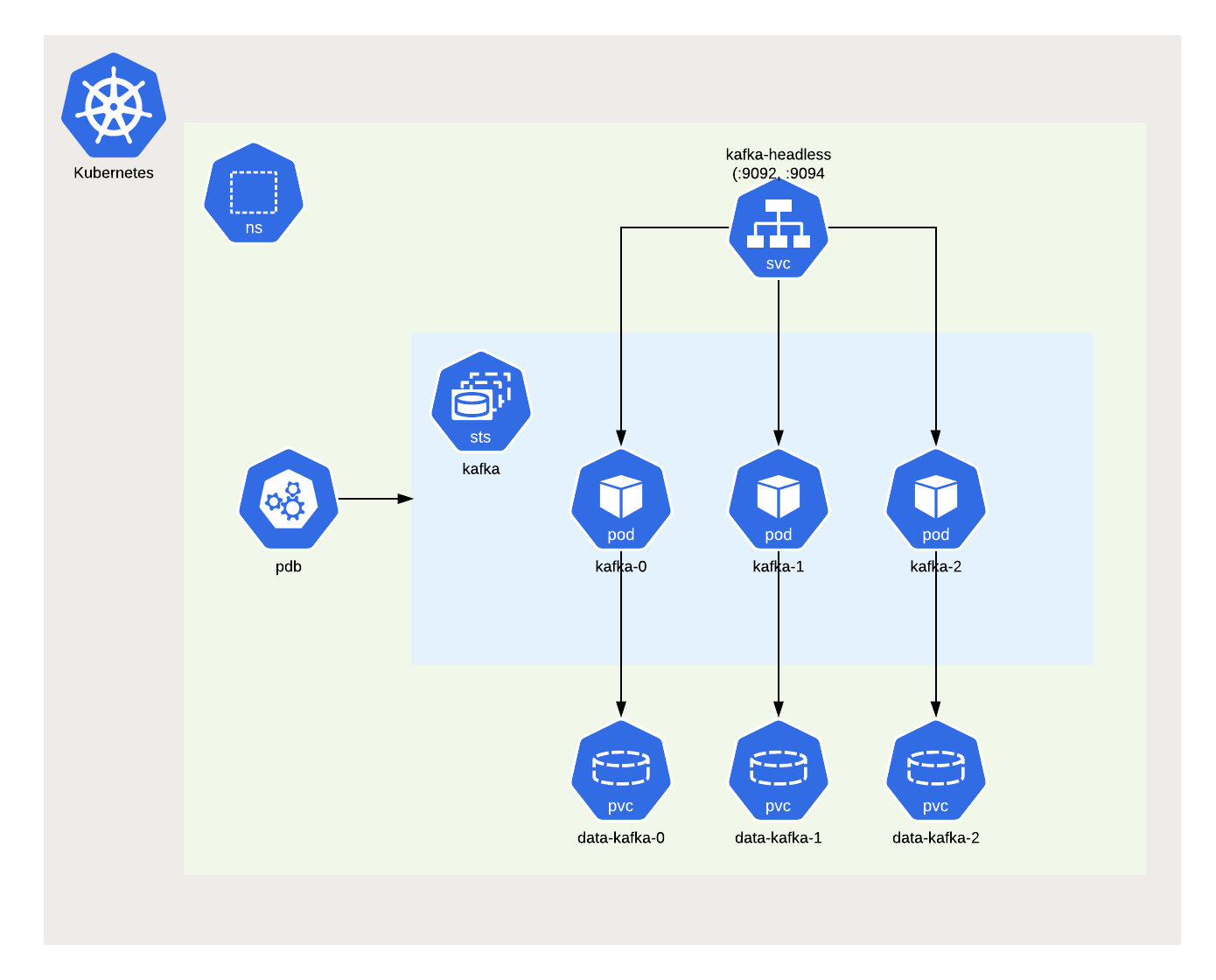
- A PodDisruptionBudget to ensure service availability during planned maintenance.
- A Headless Service to control the internal listener for the Kafka.
- A StatefulSet which contains 3 Kafka Brokers Pods, by default.
One can run the:
- helm list command to list releases installed
- helm status to display the status of the named release
- helm test to run tests for a release
To uninstall the kafka deployment run:
helm uninstall kafka
The command removes all the Kubernetes components associated with the chart and deletes the release.
Keep in mind that the PersistentVolumeClaims are in retain.
Parameters
You can specify each parameter using the --set key=value[,key=value] argument to helm install.
Alternatively, a YAML file that specifies the values for the parameters can be provided while installing the chart. For example,
helm upgrade --install kafka -f my-values.yaml rhcharts/kafka
A default values.yaml is available and should be checked for more advanced usage.
Image
By default the confluentinc/cp-kafka is in use.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
image.registry |
Registry used to distribute the Docker Image. | docker.io |
image.repository |
Docker Image of Confluent Kafka. | confluentinc/cp-kafka |
image.tag |
Docker Image Tag of Confluent Kafka. | 7.3.0 |
One can easily change the image.tag to use another version. When using a local/proxy docker registry we must change image.registry as well.
Kafka Cluster
The configuration parameters in this section control the resources requested and utilized by the kafka chart.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
replicaCount |
The number of Kafka Brokers. | 3 |
The value for the PodDisruptionBudget is always
maxUnavailableequals to1.
Confluent Kafka Broker Configuration
The next configuration related to Kafka Broker are available:
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
autoCreateTopicsEnable |
Enable auto creation of topic on the server. | false |
deleteTopicEnable |
Delete topic through the admin tool will have no effect if this config is turned off. | true |
offsetsTopicReplicationFactor |
The replication factor for the offsets topic. | 3 |
numPartitions |
The default number of log partitions per topic. | 3 |
defaultReplicationFactor |
The default replication factors for automatically created topics. | 3 |
minInsyncReplicas |
The minimum number of replicas that must acknowledge a write for the write to be considered successful. | 2 |
uncleanLeaderElectionEnable |
Indicates whether to enable replicas not in the ISR set to be elected as leader as a last resort, even though doing so may result in data loss. | false |
logFlushIntervalMessages |
The number of messages accumulated on a log partition before messages are flushed to disk | 10000 |
logFlushIntervalMs |
The maximum time in ms that a message in any topic is kept in memory before flushed to disk. | 1000 |
logRetentionBytes |
The maximum size of the log before deleting it. | 1073741824 |
logRetentionCheckIntervalMs |
The frequency in milliseconds that the log cleaner checks whether any log is eligible for deletion. | 300000 |
logRetentionHours |
The number of hours to eep a log file before deleting it (in hours). | 168 |
logSegmentBytes |
The maximum size of a single log file. | 1073741824 |
messageMaxBytes |
The largest record batch size allowed by Kafka (after compression if compression is enabled). | 1048588 |
More information can be found in the Apache Kafka Documentation and in the Confluent Documentation.
Ports used by Kafka
For those still struggling with how the listeners work take a look at Kafka Listeners - Explained by Robin Moffatt.
By default the Headless Service will expose the pods in the port 9092, port.kafkaInternal, and one can use this headless service as a Bootstrap Server.
We have setup the possibility for external access by changing the next values:
externalAccess:
enabled: true
initNodePort: 32400
## turn to support nodePort in docker desktop
isDocker: true
This will create a nodeport service that will expose each broker in a different port. So, if we have the 32400 as a start and we have 3 replicas we will have:
| pod | map |
|---|---|
kafka-0 |
9094:32400/TCP |
kafka-1 |
9094:32401/TCP |
kafka-2 |
9094:32403/TCP |
Kerberos Authentication
This chart is prepared to enable Kerberos authentication in Kafka
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
kerberos.enabled |
Boolean to control if Kerberos is enabled. | false |
kerberos.krb5Conf |
Name of the ConfigMap that stores the krb5.conf, Kerberos Configuration file |
nil¹ |
kerberos.keyTabSecret |
Name of the Secret that stores the Keytab | nil¹ |
kerberos.jaasConf |
Name of the ConfigMap that stores the JAAS configuration files per host. | nil¹ |
kerberos.testUserKeytabSecret |
Name of the Secret that stores the Keytab for the test user. Mandatory when kerberos.testUser is set |
nil |
¹ When
kerberos.enabledthese parameters are required, and the ConfigMap and Secret need to exist beforehand.
Authorization Using ACLs
This chart is prepared to enable Authorization using ACLs in Kafka but doesn’t manage ACLs.
To enable ACLs, an authentication mechanism must also be enabled, e.g. Kerberos.
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
acls.enabled |
Boolean to control if ACLs are enabled | false |
Data Persistence
The Kafka Kafka Data directory can be tweaked with:
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
data.storageClass |
Valid options: nil, "-", or storage class name. |
nil |
data.storageSize |
Size for data dir. | 10Gi |
This will allow the creation of a Persistent Volume using a specific Storage Class. However, Access Mode.
Resources for Containers
Regarding the management of Resources for Containers the next defaults regarding requests and limits are set:
With this in mind the next defaults regarding resources and limits are set:
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
resources.limits.cpu |
a container cannot use more CPU than the configured limit | 1 |
resources.limits.memory |
a container cannot use more Memory than the configured limit | 1400Mi |
resources.requests.cpu |
a container is guaranteed to be allocated as much CPU as it requests | 250m |
resources.requests.memory |
a container is guaranteed to be allocated as much Memory as it requests | 512Mi |
In terms of the JVM the next default is set:
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
heapOpts |
The JVM Heap Options for Kafka Broker. | "-XX:MaxRAMPercentage=75.0 -XX:InitialRAMPercentage=50.0" |
Advance Configuration
Check the values.yaml for more advance configuration such as: